Resources for the community pharmacy setting
| Site: | Royal College of General Practitioners - Online Learning Environment |
| Course: | TARGET antibiotics toolkit hub |
| Book: | Resources for the community pharmacy setting |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Friday, 27 February 2026, 9:16 PM |
Description

We have grouped all of the TARGET resources that are to be used in the community pharmacy setting in one place to make it easier for you to find them all.
Version 1.0, August 2022.
Overview
Community pharmacy staff play a pivotal role in antimicrobial stewardship (AMS) with their expertise in medicines and accessibility to patients.
The TARGET community pharmacy resources ensures patients receive consistent, evidence based messaging about antibiotic use, infection prevention, safety-netting and self-care advice wherever they enter the primary care pathway.
How to use pharmacy resources
Community Pharmacy Flowchart
The Community Pharmacy Flowchart acts as an aide-mémoire, highlighting which TARGET resources can be used and when, depending on where the patient is on their consultation journey.
The flowchart can be used as a leaflet for pharmacy staff or as a poster for patients. The flowchart contains images and QR codes for each leaflet and resource referenced.
TARGET Antibiotic checklist
The TARGET antibiotic checklist is for community pharmacy staff to use with patients or carers collecting antibiotics. The checklist should be completed by patients and pharmacists, to facilitate individualised advice to the patient.
TARGET Antibiotic Checklist translations
- Albanian – V2 (PDF)
- Arabic – V2 (PDF)
- Bengali – V2 (PDF)
- Farsi – V2 (PDF)
- French – V2 (PDF)
- Greek – V2 (PDF)
- Gujarati – V2 (PDF)
- Hindi – V2 (PDF)
- Hungarian – V2 (PDF)
- Italian – V2 (PDF)
- Kurdish Sorani – V2 (PDF)
- Lithuanian – V2 (PDF)
- Polish – V2 (PDF)
- Portuguese – V2 (PDF)
- Punjabi (Gurmukhi) – V2 (PDF)
- Romanian – V2 (PDF)
- Simplified Chinese – V2 (PDF)
- Somali – V2 (PDF)
- Spanish – V2 (PDF)
- Swahili – V2 (PDF)
- Tamil – V2 (PDF)
- Tigrinya – V2 (PDF)
- Traditional Chinese – V2 (PDF)
- Turkish – V2 (PDF)
- Urdu – V2 (PDF)
- Welsh - V2 (PDF)
Community pharmacy counselling checklist
This Antibiotic Prescription Screening and Counselling sheet is a supporting tool to help inform the information provided to patients, including how to take antibiotics and their common side effects. This sheet summarises information from the British National Formulary (BNF) and Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC) and can support pharmacy teams and other healthcare professionals when screening an antibiotic prescription. Please refer to the accompanying user guide for this resource on how to use it.
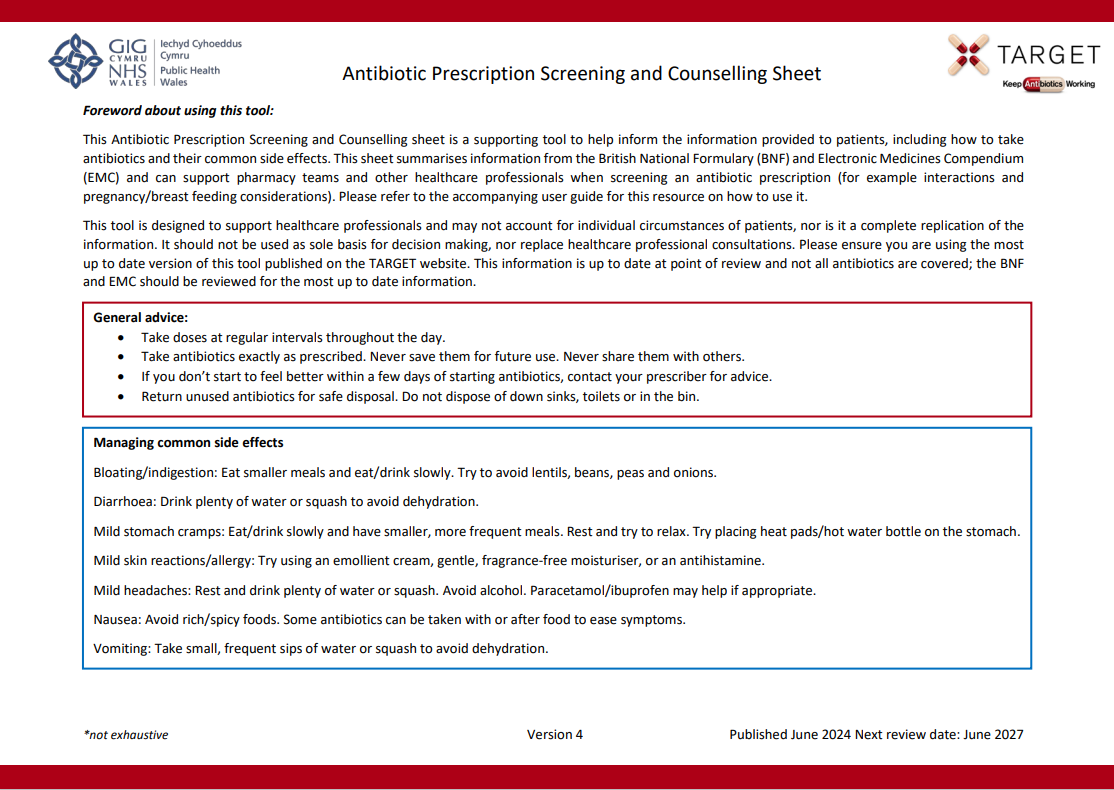
- Antibiotic Prescription Screening and Counselling Sheet V4 (PDF file, 283 KB)
- Antibiotic prescription screening and counselling sheet user guide V1 (PDF file, 124 KB)
For more information on How Community Pharmacies Can Keep Antibiotics Working, visit Health Education England’s AMR Hub and complete the e-module on Antimicrobial Stewardship for Community Pharmacy.
For any queries in the content of the leaflet please contact us: TARGETantibiotics@ukhsa.gov.uk
UTI Women Under 65 Leaflet for community pharmacies
The Treating Your Infection Urinary Tract Infection (TYI-UTI) leaflet for community pharmacies has been designed to be used with women under 65 years who are experiencing urinary symptoms suggesting uncomplicated UTIs. This leaflet supports implementation of recommendations in the NICE guidelines on processes for antimicrobial stewardship and behaviour change for antimicrobial stewardship.
Patient Information Leaflets for Community Pharmacy
UTI Women Under 65 Leaflet
- UTI for women under 65 leaflet for community pharmacies V1 (DOCX file, 71 KB)
- UTI for women under 65 leaflet for community pharmacies V1 (PDF file, 142 KB)
- UTI for women under 65 leaflet for community pharmacies fully referenced V1 (PDF file, 274 KB)
- UTI for women under 65 leaflet for community pharmacies user guide V1 (DOCX file, 3,476 KB)
- UTI for women under 65 leaflet for community pharmacies (Welsh) V1 (PDF file, 103 KB)
UTI pharmacy leaflet HTML

For community pharmacy
Contents
- Possible urinary signs and symptoms
- Outcomes and recommended care
- When should you get help?
- Self-care to help yourself get better more quickly
- Options to help prevent a UTI
- Antibiotic resistance
- About this leaflet
Possible urinary signs and symptoms
Key signs/symptoms
- Dysuria: Burning pain when passing urine (wee)
- New nocturia: Needing to pass urine in the night
- Cloudy urine: Visible cloudy colour when passing urine
Other signs/symptoms to consider
- Frequency: Passing urine more often than usual
- Urgency: Feeling the need to pass urine immediately
- Haematuria: Blood in your urine
- Suprapubic pain: Pain in your lower tummy
Other things to consider
Recent sexual history
- Inflammation due to sexual activity can feel similar to the symptoms of a UTI
- Some sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can have symptoms similar to those of a UTI
Changes during menopause
- Some changes during the menopause can have symptoms similar to those of a UTI
Outcomes and recommended care
When should you get help?
Contact your GP practice or contact NHS
Phone for advice if you are not sure how urgent the symptoms are.
- You have shivering, chills and muscle pain
- You feel confused, or are very drowsy
- You have not passed urine all day
- You are vomiting
- You see blood in your urine
- Your temperature is above 38°C* or less than 36°C
- You have kidney pain in your back just under the ribs
- Your symptoms get worse
- Your symptoms are not starting to improve within 48 hours of taking antibiotics
Self-care to help yourself get better more quickly
- Drink enough fluids to stop you feeling thirsty. Aim to drink 6 to 8 glasses
- Avoid too much alcohol, fizzy drinks or caffeine that can irritate your bladder
- Take paracetamol or ibuprofen at regular intervals for pain relief, if you have had no previous side effects
- There is currently no evidence to support taking cranberry products or cystitis sachets to improve your symptoms
- Consider the risk factors in the ‘Options to help prevent UTI’ section to reduce future UTIs
Options to help prevent a UTI
It may help you to consider these risk factors:
- Stop bacteria spreading from your bowel into your bladder. Wipe from front (vagina) to back (bottom) after using the toilet
- Avoid waiting to pass urine. Pass urine as soon as you need to
- Go for a wee after having sex to flush out any bacteria that may be near the opening to the urethra
- Wash the external vagina area with water before and after sex to wash away any bacteria that may be near the opening to the urethra
- Drink enough fluids to make sure you wee regularly throughout the day, especially during hot weather
If you have a recurrent UTI, the following may help:
- Cranberry products and D-mannose: There is some evidence to say that these work to help prevent recurrent UTI
- After the menopause: Topical hormonal treatment may help; for example, vaginal pessaries
- Antibiotics at night or after sex may be considered
Antibiotic resistance
- Antibiotics can be lifesaving. But antibiotics are not always needed for urinary symptoms
- Antibiotics taken by mouth, for any reason, affect our gut bacteria making some resistant
- This may make future UTI more difficult to treat
- Common side effects to taking antibiotics include thrush, rashes, vomiting and diarrhoea. Seek medical advice if you are worried
- Keep antibiotics working; only take them when advised by a health professional. This way they are more likely to work for a future UTI
About this leaflet
TARGET is operated by the UK Health Security Agency. Developed in collaboration with professional medical bodies.
Version: 1
Published: September 2022
Review: September 2025
RTI leaflet for community pharmacies
The Treating Your Infection Respiratory Tract Infection (TYI-RTI) Pharmacy leaflet has been designed to be used with patients who are experiencing self limiting RTIs. This leaflet supports implementation of recommendations in the NICE guidelines on processes for antimicrobial stewardship, behaviour change for antimicrobial stewardship and antibiotic prescribing for respiratory tract infections.
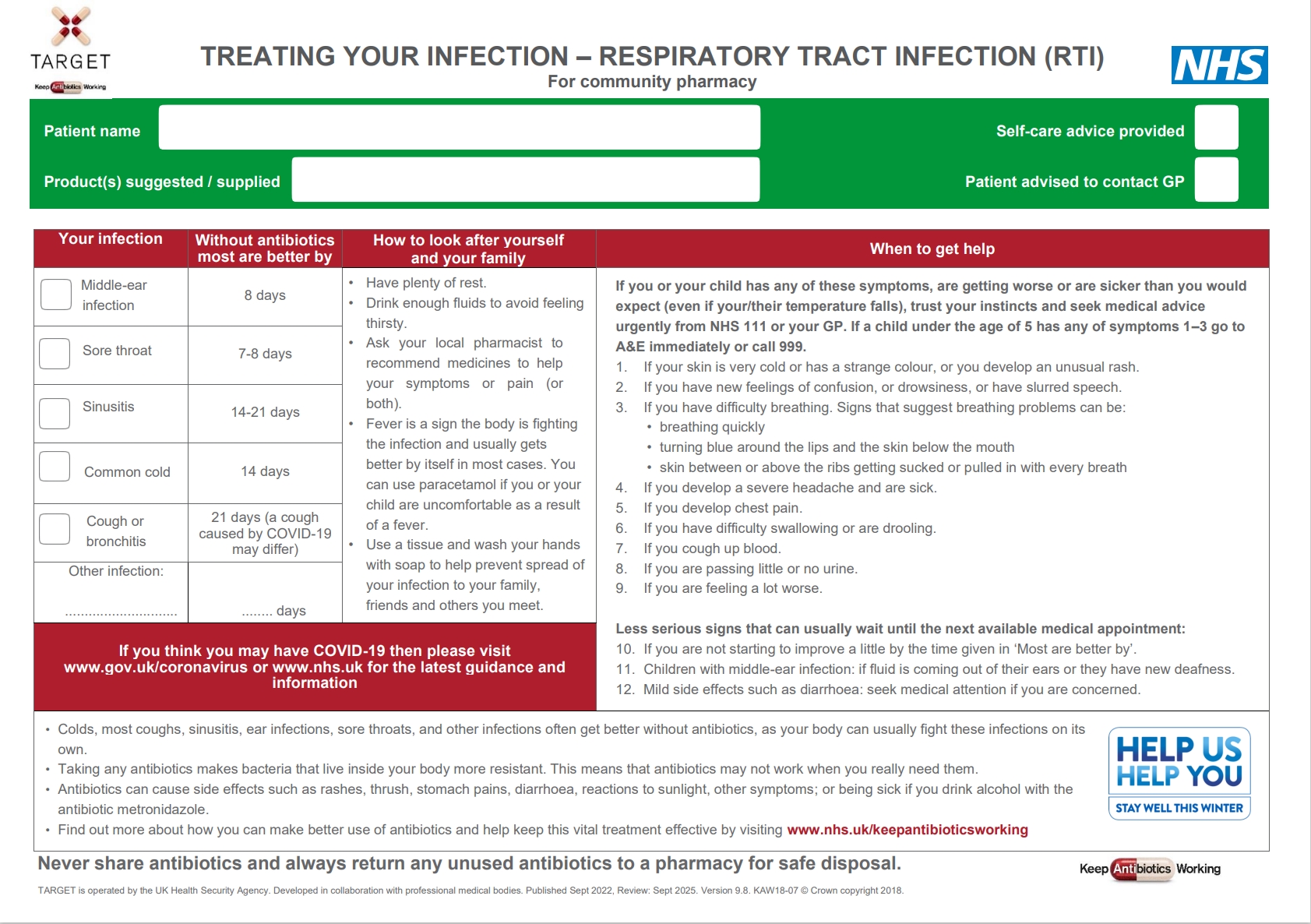
Patient Information Leaflets for Community Pharmacy
RTI leaflet
- RTI leaflet for community pharmacies – V9.8 (DOCX file, 91 KB)
- RTI leaflet for community pharmacies – V9.8 (PDF file, 170 KB)
- RTI leaflet for community pharmacies fully referenced V1 (PDF file, 274 KB)

RTI leaflet (Welsh) – Version 9.7
- RTI leaflet for community pharmacies (English for those living in Wales) V9.8 (PDF file, 139 KB)
- RTI leaflet for community pharmacies (Welsh for those living in Wales) V9.8 (PDF file, 216 KB)
- RTI leaflet for community pharmacies (Welsh for those living in England) V9.8 (PDF file, 211 KB)
Caring for children with coughs leaflet
This leaflet was not developed by TARGET/UKHSA but may be useful to share in community pharmacy settings. The Caring for children with coughs leaflet was co-created by a diverse group of parents and University of Bristol researchers. It contains information addressing the four most common parental concerns for children with RTI with cough and safety-netting advice based on NICE guidelines. It was validated as part of a trial to improve prescribing for cough in children.
RTI pharmacy leaflet HTML

For community pharmacy
Contents
- Your infection
- How to look after yourself and your family
- When to get help
- Consider COVID-19
- About antibiotics
- About this leaflet
Your infection
Middle-ear infection
Without antibiotics, most are better by 8 days.
Sore throat
Without antibiotics, most are better by 7-8 days.
Sinusitis
Without antibiotics, most are better by 14-21 days.
Common cold
Without antibiotics, most are better by 14 days.
Cough or bronchitis
Without antibiotics, most are better by 21 days (a cough caused by COVID-19 may differ).
How to look after yourself and your family
- Have plenty of rest.
- Drink enough fluids to avoid feeling thirsty.
- Ask your local pharmacist to recommend medicines to help your symptoms or pain (or both).
- Fever is a sign the body is fighting the infection and usually gets better by itself in most cases. You can use paracetamol if you or your child are feeling uncomfortable as a result of a fever.
- Use a tissue and wash your hands with soap to help prevent spread of your infection to your family, friends and others you meet.
When to get help
Serious signs and symptoms
If you or your child has any of these symptoms, are getting worse or are sicker than you would expect (even if your/their temperature falls), trust your instincts and seek medical advice urgently from NHS 111 or your GP. If a child under the age of 5 has any of symptoms 1–3 go to A&E immediately or call 999.
- If your skin is very cold or has a strange colour, or you develop an unusual rash.
- If you have new feelings of confusion or drowsiness, or have slurred speech.
- If you have difficulty breathing. Signs that suggest breathing problems can be:
- breathing quickly
- turning blue around the lips and the skin below the mouth
- skin between or above the ribs getting sucked or pulled in with every breath.
- If you develop a severe headache and are sick.
- If you develop chest pain.
- If you have difficulty swallowing or are drooling.
- If you cough up blood.
- If you are passing little or no urine.
- If you are feeling a lot worse.
Less serious signs that can usually wait until the next available appointment
- If you are not starting to improve a little by the time given in ‘Your infection’, above
- Children with middle-ear infection: if fluid is coming out of their ears or they have new deafness
- Mild side effects such as diarrhea: seek medical attention if you are concerned.
COVID-19 specific advice
If you think you may have COVID-19 then please visit GOV.UK's coronavirus section and the NHS for the latest guidance and information.
Advice about antibiotics
- Colds, most coughs, sinusitis, ear infections, sore throats, and other infections often get better without antibiotics, as your body can usually fight these infections on its own.
- Taking any antibiotics makes bacteria that live inside your body more resistant. This means that antibiotics may not work when you really need them.
- Antibiotics can cause side effects such as rashes, thrush, stomach pains, diarrhoea, reactions to sunlight, other symptoms; or being sick if you drink alcohol with the antibiotic metronidazole.
- Find out more about how you can make better use of antibiotics and help keep this vital treatment effective by visiting the NHS antibiotics webpages.
Never share antibiotics and always return any unused antibiotics to a pharmacy for safe disposal.
About this leaflet
TARGET is operated by the UK Health Security Agency. Developed in collaboration with professional medical bodies.
Version: 1
Published: September 2022
Review: September 2025
Other TARGET leaflets that can be used in community pharmacy
Self-care leaflet
The Managing Your Common Infection (Self-Care) leaflet can be used as a tool to increase patients’ confidence and knowledge on how to self-care for their own infections thereby potentially reduce inappropriate antibiotic use.
This resource can be used in all settings, please find the link to the different versions below:
- Leaflets to discuss with patients: Self-care leaflet (rcgp.org.uk)
- Leaflets to discuss with patients: Self-care leaflet HTML (rcgp.org.uk)
UTI combined leaflet
This leaflet contains information from our Treating Your Infection Urinary Tract Infection (TYI-UTI) leaflet for women under 65 years and UTI leaflet for older adults in an easily accessible booklet style format with icons and images. This leaflet has been designed for use in the primary care setting, including general practice, community pharmacy and for use by carers and in care homes. It is suitable for consultations to facilitate dialogue between a patient or their carer and their healthcare professional on specific topics related to managing their UTI.
- Leaflets to discuss with patients: UTI Leaflet - Combined For Adults (rcgp.org.uk)
- Leaflets to discuss with patients: UTI Leaflet - Combined For Adults HTML (rcgp.org.uk)
RTI Pictorial leaflet
The leaflet can be used to provide information on RTIs. It is pictorial and uses plain English so that it is suitable for a range of community groups. The leaflet may also be used during primary care consultations to facilitate dialogue between a patient and their healthcare professional on specific topics like treatment or safety netting. We would recommend that the leaflet is used as a tool to interact with patients, rather than as a ‘parting gift’.